Circular Singly Linked List
In a circular Singly linked list, the last node of the list contains a pointer to the first node of the list. We can have circular singly linked list as well as circular doubly linked list.
We traverse a circular singly linked list until we reach the same node where we started. The circular singly liked list has no beginning and no ending. There is no null value present in the next part of any of the nodes.
The following image shows a circular singly linked list.
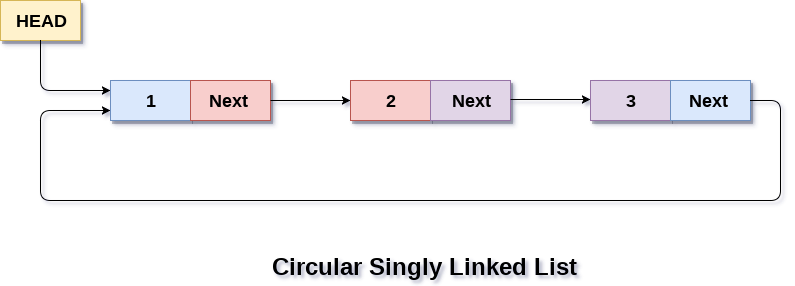
Circular linked list are mostly used in task maintenance in operating systems. There are many examples where circular linked list are being used in computer science including browser surfing where a record of pages visited in the past by the user, is maintained in the form of circular linked lists and can be accessed again on clicking the previous button.
Memory Representation of circular linked list:
In the following image, memory representation of a circular linked list containing marks of a student in 4 subjects. However, the image shows a glimpse of how the circular list is being stored in the memory. The start or head of the list is pointing to the element with the index 1 and containing 13 marks in the data part and 4 in the next part. Which means that it is linked with the node that is being stored at 4th index of the list.
However, due to the fact that we are considering a circular linked list in the memory, therefore, the last node of the list contains the address of the first node of the list.
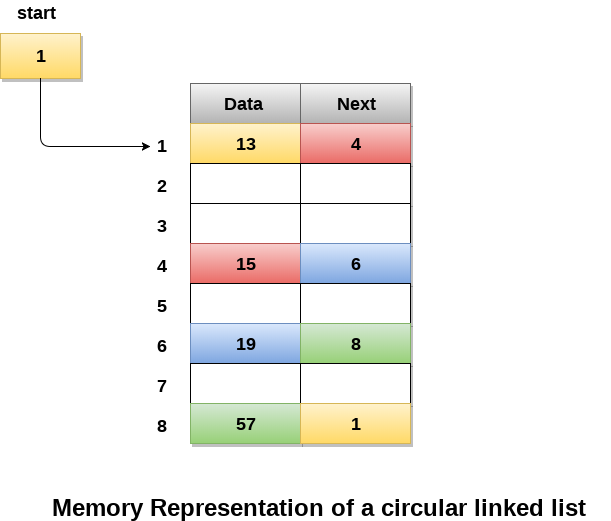
We can also have more than one number of linked list in the memory with the different start pointers pointing to the different start nodes in the list. The last node is identified by its next part which contains the address of the start node of the list. We must be able to identify the last node of any linked list so that we can find out the number of iterations which need to be performed while traversing the list.
Operations on Circular Singly linked list:
Insertion
| SN | Operation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Insertion at beginning | Adding a node into circular singly linked list at the beginning. |
| 2 | Insertion at the end | Adding a node into circular singly linked list at the end. |
Deletion & Traversing
| SN | Operation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Deletion at beginning | Removing the node from circular singly linked list at the beginning. |
| 2 | Deletion at the end | Removing the node from circular singly linked list at the end. |
| 3 | Searching | Compare each element of the node with the given item and return the location at which the item is present in the list otherwise return null. |
| 4 | Traversing | Visiting each element of the list at least once in order to perform some specific operation. |
